Sorting months and time periods correctly is one of the most common challenges in Power BI. By default, Power BI sorts text fields alphabetically, which often results in incorrect month or period order in visuals.
This guide walks through step-by-step solutions using a Date table, covering:
- Month sorting
- Month-Year sorting
- Custom week-year sorting
Custom Sort in Power BI:
Each example follows the same flow:
- Identify the sorting issue
- Fix it using the Date table
- Confirm the correct order in visuals
-
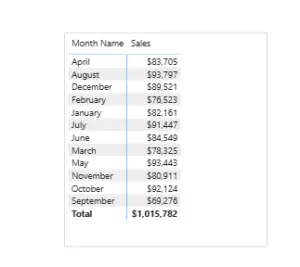
The Problem: Months Sorting Incorrectly
When month names are used directly in visuals, Power BI sorts them alphabetically instead of chronologically.
For example, months may appear as:
-
Important Note: Power BI’s Automatic Date Hierarchy
Power BI automatically detects date columns and creates a built-in date hierarchy (Year → Quarter → Month → Day).
When this automatic hierarchy is used, Power BI internally sorts dates correctly.
However, using this auto-generated date hierarchy is not recommended because:
- You cannot define custom week logic
- You cannot control sorting logic
- It breaks data model clarity
- It limits advanced time intelligence
- It creates multiple hidden date tables behind the scenes
Best Practice
Always use a dedicated Date table instead of relying on Power BI’s automatic date hierarchy.
-
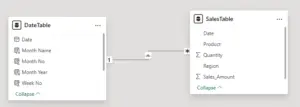
Creating and Using a Date Table
To control time-based sorting, a dedicated Date table is essential. The Date table allows you to store numeric values (such as month number or year) that can be used for proper sorting.
-
Sorting Month Names Using Month Number
Month names should always be sorted using a numeric month column from the Date table.
The approach is:
- Month Name remains a text column
- Month Number is used as the sorting column
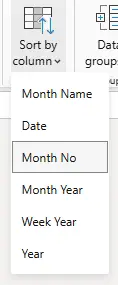
- Power BI’s Sort by Column feature is applied
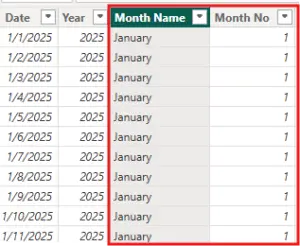
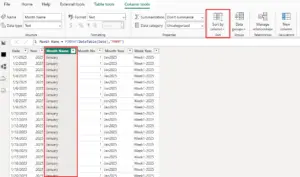
Here, the Month Name column is selected in the Fields pane.
In the Column tools ribbon, the Sort by Column option becomes available.
This feature allows Power BI to sort a text column using another column from the same table.
In this step, the Month Name column is explicitly sorted by the Month Number column.
Once applied, Power BI permanently associates Month Name with its numeric month order.
-
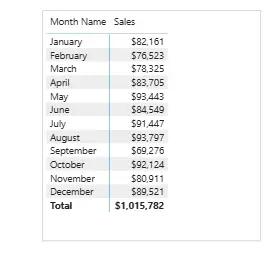
Verifying the Sorted Month Visual
After applying the correct sorting, visuals will now display months in proper chronological order.
-
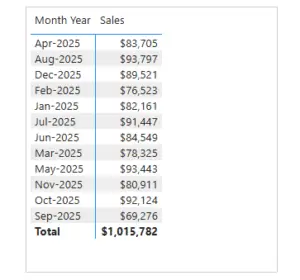
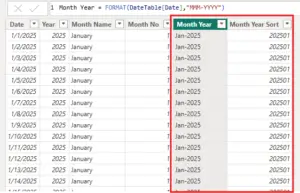
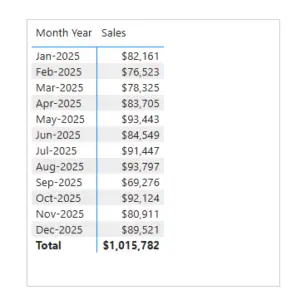
Sorting Month-Year Correctly
Month-Year fields also sort alphabetically if treated as text.
Example:
To fix this:
- Use a numeric Month -Year column in the Date table
- Sort the Month-Year text column by this numeric value
-
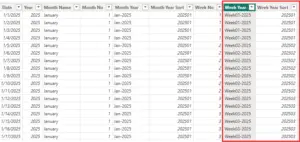
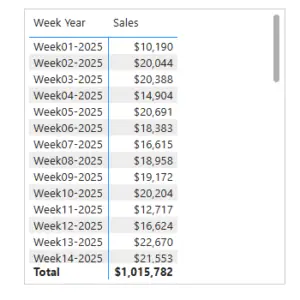
Sorting Custom Week-Year Values
Week-Year fields (such as W01-2024) can also sort incorrectly when treated as text.
To resolve this:
- Use a numeric Week-Year or sequential week index
- Apply Sort by Column using that numeric field
This ensures weeks appear in correct chronological order across years.
👉 Join our Power BI Training and gain hands-on skills to turn insights into action.
Final Notes
Correct sorting in Power BI is not achieved through formatting alone.
It requires a structured Date table, numeric sort columns, and proper use of Sort by Column.
This approach ensures consistent, accurate, and scalable time-based reporting across all visuals.