The Difference between Database and Data Warehouse
Global Data 365 is composed of highly skilled professionals who specialize in streamlining the data and automate the reporting process through the utilization of various business intelligence tools.
For corporations of all sizes and sectors, the world of Big Data keeps expanding. The performance and profitability of any business rely mainly on the volume, consistency, and reports of the information they gather and how well the companies will analyse, gain input from, and take action on the data they have collected. It is not easy to transform the raw data collected into valuable insights.
It requires organizations to learn the practice of corporate data management so that workers can effectively produce, archive, view, handle and interpret the data they need to succeed at their work. So, when it comes to gathering, storing, and analysing data, what could prove to be the right decision for your company? The most common types of data storage in enterprise data management are databases and data warehouses. So what is the difference between a database and a data warehouse, and which one is the right choice for your company?
What is a Database?
By definition, a database is a systematic collection of data gathered in a way that makes common sense and makes data search, storage, manipulation, and analysis easier. Typically, databases contain data assembled in rows, columns, and tables, arranged primarily for easy insight and the collection of various events. The most common type of organizing databases is SQL (relational), NoSQL (non-relational), CRM systems, and Excel spreadsheets.
Databases contain multiple tables, each of which consists of columns and rows. Every column is appointed to an element, and a single record is held in every row. To browse through a relational database, users type questions in Structured Query Language (SQL), a domain-specific language for database communication.
It is possible to store databases either on a local server or in the cloud and access them for reporting in various ways through the system’s limited native tools that are integrated with the data collection itself to Excel exports or different options for direct connectivity. Using SQL to write queries can be a huge benefit for productivity and easy use, but in terms of data hierarchy, relational databases are often less versatile and more static.
What is a Data Warehouse?
Data Warehouse can be defined as a system that collects and stores data from several diverse resources within an enterprise. In comparison to a database, a data warehouse’s infrastructure is designed to get the data out, and not just by technical tools, but for regular users like finance professionals, executives, management, and other workers.
The objective of a data warehouse is specifically business-oriented: it is intended to promote decision-making by enabling end-users to consolidate and interpret data from multiple sources. Being the basis for BI and analytics, it takes out information from existing databases, defines a series of rules to covert the data, and then transferring it into a single central repository to view and manage easily.
A data warehouse stores information of the transfer level and supports the larger reporting and analytical needs of an organization, providing one basis of reality for building semantic models or the provision of organized, simplified, and aligned data for tools, such as Excel, Power BI, or even SSRS. Companies that have a higher level of data or analytical needs tend to use a data warehouse. Regular data transactions like standard costing, currency conversions, unit of measure conversions, and other business approved and permitted calculations are all integrated into the data warehouse by making sure that reports reflect the desirable data. The only drawback to a data warehouse is that it is complicated, time-consuming, and costly to construct and maintain.
Key Differences between Database and Data Warehouse
With more volume and complexity of data used in the organizations, they want to receive more analytical insight, which is why data warehouses are receiving more visibility for database reporting and analytics. The key distinction is that databases contain accumulated data that are organized. Whereas data warehouses are data systems constructed from various information sources, as they are used to analyse information.
Below are some more differences that further distinguishes database and data warehouse from each other.
– Databases use OLTP Solutions, whereas data warehouses are better suited for OLAP solutions.
– Databases are designed to manage thousands of users at a time. Due to their complex structure, data warehouses can only manage a small amount of data users.
– For small, atomic transfers databases are more useful. Data warehouses are equipped for larger queries that need greater analysis.
– Downtime of databases can be costly, as they need to function all the time. Data warehouses are not compromised by downtime.
– For CRUD operations, databases are configured to be quick in creating, reading, updating, and deleting data. Data Warehouses are configured for a limited number of complex queries over several large data stores.
– Databases are organized as effectively as required, with multiple tables without duplicate data. Usually, data warehouses denormalize their information, valuing reading operations over-writing operations.
– Usually, databases store only the updated data, which makes it impossible for old queries. Data Warehouses have been constructed solely for reporting and analysis.
Interact Live
with Dashboards
Increase efficiency and deliver success now with Microsoft Power BI. Enjoy a 20% discount on all Power BI services.
Interact Live
with Dashboards
Increase efficiency and deliver success now with Microsoft Power BI. Enjoy a 20% discount on all Power BI services.

Importance of Databases and Data Warehouses for Businesses
Companies can reap the benefits of both databases and data warehouses for reporting and analysis in different ways. Let’s see why:
Data Quality and Accuracy
Data warehouse includes transferring information from different sources, standardising it, naming it, arranging it, and making sure the uniform restrictions are sorted and labelled. This ensures better confidence in the information being displayed, minimizes organizational errors, and gives better possibilities for partnership as independent business sectors like sales, marketing, and finance all depend on similar reporting from the data repository.
Power Business Intelligence
One of the greatest advantages of data warehousing is the rising scope and efficiency of data storage. By optimising access to the data of your organization, you are strengthening the leadership’s willingness to adopt a smarter plan centred on a more complete and effective solution. Data warehouse-powered business intelligence provides deeper insight into sales operation, financial stability, and much more.
Increased ROI
The use of data warehousing helps organizations to save money on their analytics, and as a result, a larger amount of profit is generated. As the expense of data warehousing reduces, this effect grows exponentially, and by using BI software and data warehousing in coordination to effectively democratise data and slash headcount in reporting and analytics operations, companies can generate a return on investment faster.
Improved Efficiency
Data warehouses are designed for speed, in particular to providing large businesses quick access to retrieval and analysis of data. Instead of devoting useful numerical data, data warehouses are all about the ability to edit and maintain specific data records. By making sure that the data can be obtained, collated, and processed as easily as possible, the process of making important business decisions in an instant becomes easier.
Best Way to Build a Data Warehouse
It is popularly known that there are as many ways to create data warehouses as there are companies to develop them. Every data warehouse is special, as it adheres to the requirements of business users in numerous functional areas in which firms face diverse market environments and competitive forces.
Creating the Staging Area
Before analysis of the data, it goes through the process of retrieval, conversion, and loading of data. As the warehouse is as strong as the data stored within it, for the success of your company it needs to match department requirements and objectives.
Building an Environment
Usually, data warehouses have three main physical settings: development, testing, and manufacturing. And these three settings will exist on entirely different physical services.
Data Modelling
Data Modelling is the process of visualizing the distribution of data in your data warehouse. Before constructing a data warehouse, it is important to know where and why data goes. This is why data modelling is used.
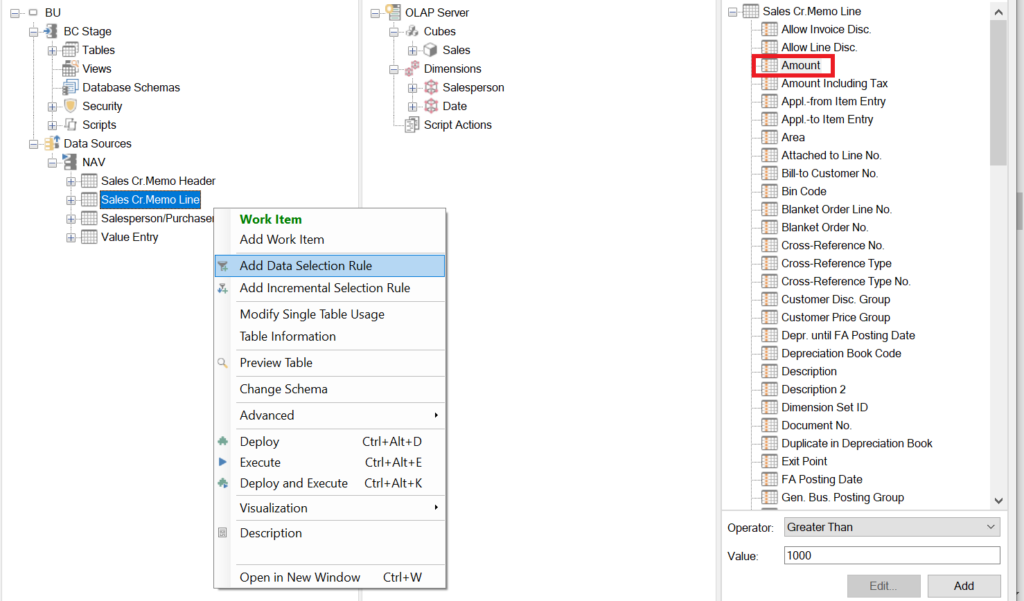
Choosing Your Extract, Transfer, Load Solution
ETL Solution is the process you will use to extract data from your existing storage solution and place it in your warehouse. That is why it is pertinent to carefully choose the right ETL solution for your warehouse.
Create Front-End
It is important to have front-end visualization, so users can instantly comprehend and utilize the results of data queries. BI tools like Power BI work best for visualization, and you can also customize your own solution.
Queries Optimized
Having your queries optimized is a complicated process that answers your required needs. Make sure that your manufacturing, testing, and development setting have similar resources to prevent lagging.
Conclusion
Database and data warehouse serve different functions in practice. If you are contemplating about building your own data warehouse or database, then it is one indication that the organization is dedicated to the practice of effective corporate data management.
Every company has different needs to build a data warehouse, which is why Global Data 365 designed a reporting and BI solution that provides the user with a pre-built data warehouse and cubes set ready to be used. With a wide dashboard library and report templates, Jet Analytics is built to provide you useful insight day one into your results. In the years to come, the accuracy, durability, and usability of data will be the key differentiator for firms of all types. That is why organizations would want to make sure that they are placing themselves up for sustainable growth by selecting the best infrastructure and storage.
To know more about data warehouse and how you can implement it in your business, contact us now.


Pingback: Jet Basics vs Jet Reports - Should You Upgrade? - Global Data 365
Pingback: Jet Analytics Data Warehouse as a Future-Proof Business Solution - Global Data 365
Pingback: Why BI Implementation Can Be Risky? - Global Data 365