A Complete Guide on Microsoft 365 Copilot
Microsoft 365 Copilot: Revolutionizing Your Productivity

- Global Data 365
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital productivity tools, Microsoft 365 stands tall as a comprehensive suite that empowers businesses worldwide. Among its many offerings, Microsoft 365 Copilot emerges as a transformative solution, promising to revolutionize the way organizations manage their Microsoft 365 environment.
What is Microsoft 365 Copilot?
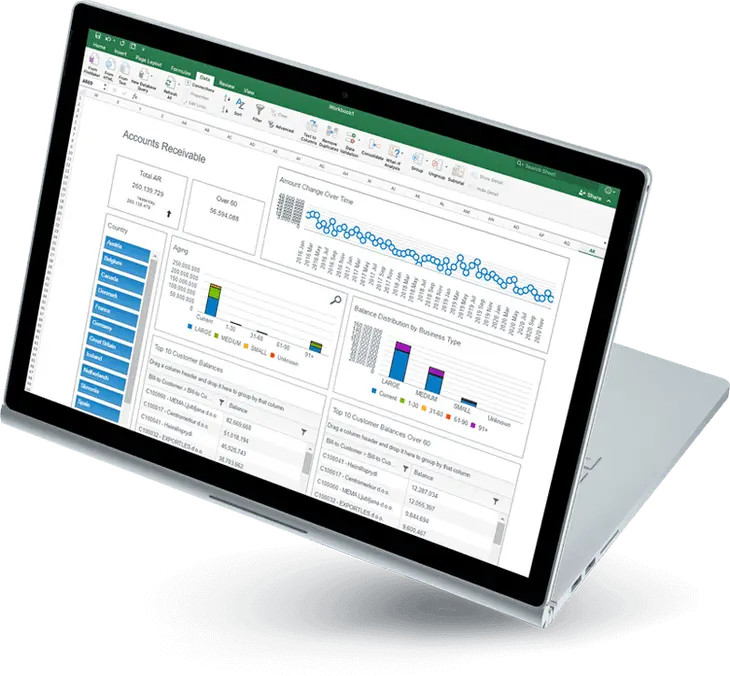
Microsoft 365 Copilot is a revolutionary management tool designed to simplify the administration of Microsoft 365 services including those crucial for customer relationship management (Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM), finance and operations (Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O), and business central management (Microsoft Dynamics 365 BC).
It comprises three main components: Microsoft 365 apps (like Word, Excel, Teams), Microsoft Graph (incorporating files and data across the M365 environments), and OpenAI models (including ChatGPT-3, ChatGPT-4, DALL-E, Codex, and Embedding), all hosted on Microsoft Azure. Unlike traditional management methods, Copilot offers a more efficient and streamlined approach, allowing organizations to focus on their core business activities.
Microsoft 365 Copilot Features:
The Copilot offers many features for vast business community such as;
- Effortless Automation: Microsoft 365 Copilot improves productivity by automating repetitive tasks and workflows, allowing employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Reduced Cost and optimizing Resources: It helps organizations save costs and optimize resources by streamlining Microsoft 365 management processes.
- AI-powered insights: It leverages AI to unlock valuable insights from your Dynamics 365 state. Gain real-time customer behavior trends in Dynamics 365 CRM or identity financial optimization opportunities in Dynamics 365 F&O.
- Streamlined Collaboration: Microsoft 365 Copilot fosters seamless collaboration within Dynamics 365 applications. Imagine teams working together on sales proposals in Dynamics 365 CRM or project plans in Dynamics 365 Business Central with real-time edits and suggestions.
- Enhanced Security: It empowers businesses to maintain robust security within Dynamics 365. Leverage advanced monitoring and threat detection to keep your data safe.
How Much Does Microsoft 365 Copilot Cost?
Microsoft 365 Copilot is available as part of the Microsoft 365 Enterprise subscription, which offers a range of plans tailored to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. The cost of Copilot varies depending on the specific plan chosen, with pricing starting at $30 per user per month for the basic plan. Find how Microsoft Dynamics transform your business with: Microsoft 365. Future plans include tailored Microsoft 365 Copilot for Dynamics 365, Power Platform, security suite, and Windows OS.
How many Modes of Interaction are in Copilot?
- Microsoft 365 Copilot system offers two main interaction modes: Direct engagement within applications like Word and Teams, and accessibility through Microsoft 365 Chat in Teams
- Within applications, users seamlessly integrate M365 Copilot for tasks like drafting documents and summarizing meetings in real-time.
- The second method of interaction is through Microsoft 365 Chat, functioning as a chatbot within Teams. Microsoft 365 Chat serves as a versatile tool for natural language interactions, enabling users to search across diverse sources.
- Microsoft 365 Copilot enhances productivity in Word by offering text suggestions, facilitates collaboration in Teams with real-time meeting summaries, and streamlines PowerPoint presentations.
- In addition to automation, Microsoft 365 Copilot also provides advanced monitoring and reporting capabilities, allowing you to keep track of service health and performance metrics. This information can help you identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring that your Microsoft 365 copilot environment remains stable and reliable.
In Conclusion
Copilot is a transformative tool that empowers businesses to unlock the full potential of Dynamics 365. With its innovative cutting-edge functionality and user-friendly interface, Copilot is empowering teams to collaborate more effectively and achieve their goals efficiently. To experience the benefits of Microsoft 365 Copilot for your business and drive growth, contact us at Global Data 365 today. Our team is ready to help you leverage this powerful tool to take your productivity to new heights.
Get 30 days free license for Jet Reports
Search Blog
Related Resources
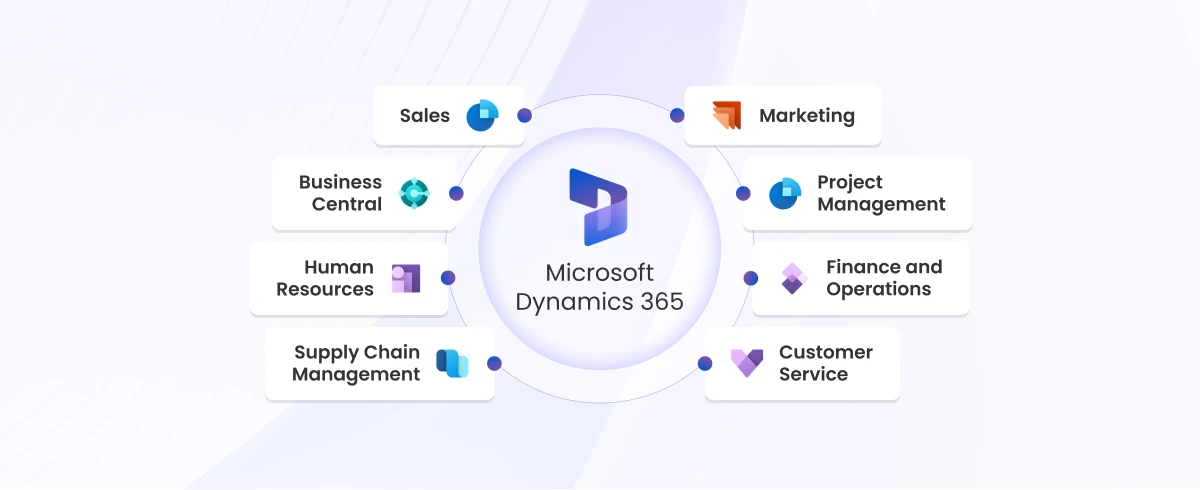
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Solution: Driving Digital Transformation
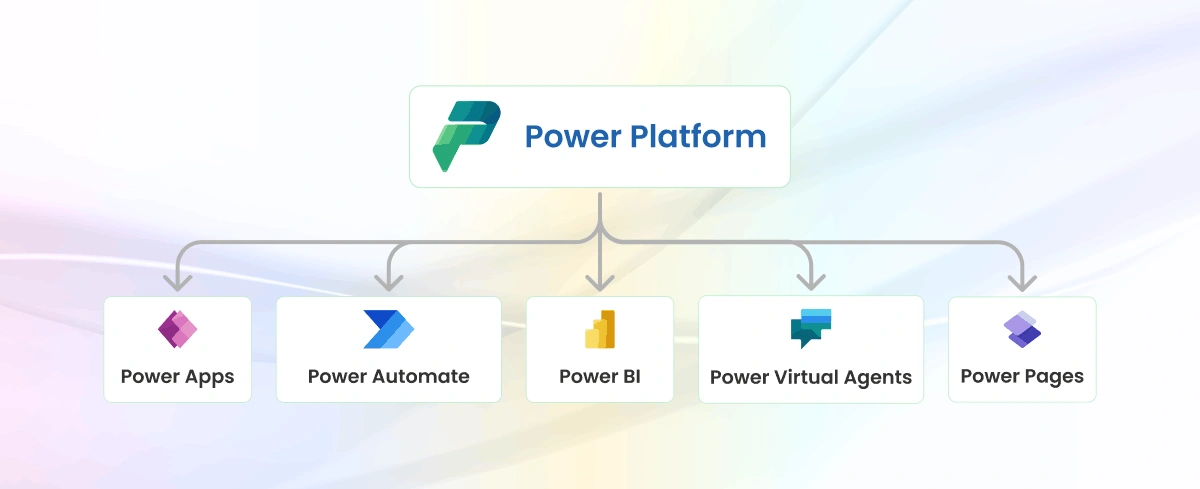
What is Microsoft Power Platform?

Migrating from On-Premise ERP to Microsoft Dynamics 365
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Microsoft 365 Copilot: Revolutionizing Your Productivity Read More »