Improving Data Readiness in Dynamics 365 Projects
Improving Data Readiness in Dynamics 365 Projects

- Global Data 365
Implementing Microsoft Dynamics 365 is often seen as a major step toward digital transformation. Organizations invest significant time and resources into configuring modules, training teams, and planning their go live strategy.
Yet many projects run into unexpected delays or performance issues for a much simpler reason: the data is not ready.
Data readiness rarely gets the same attention as system architecture or integrations, but it plays a central role in whether a Dynamics 365 project succeeds or struggles. When data is inconsistent, incomplete, or stored in incompatible formats, even the most advanced ERP platform cannot deliver the insights and efficiency businesses expect.Preparing data properly before and during implementation can dramatically improve project outcomes and make reporting, analytics and day to day operations far smoother.
What Data Readiness Means in Dynamics 365?
Data readiness goes far beyond simply cleaning up a spreadsheet before importing it into the system.
In the context of Dynamics 365, it involves ensuring that data is structured, consistent, and compatible with the platform and the reporting tools connected to it. This includes having standardized formats across datasets, clear definitions for key fields, and consistent master data such as customers, vendors, products, and financial accounts. Historical data that needs to be migrated should be validated and structured in a way that aligns with Dynamics data models.
Another important element is making sure the data will support reporting and analytics tools like Power BI or Jet Reports. When datasets are properly organized from the beginning, reporting becomes faster and more reliable, which ultimately helps teams make better decisions.
Organizations that approach data readiness strategically often find that their Dynamics implementation runs more smoothly and produces value sooner.
Common Data Challenges During Dynamics 365 Implementations
In many projects, data problems start long before the first migration takes place. Legacy systems, spreadsheets, and manual processes often produce datasets that were never designed to work together.
Companies frequently discover that their data exists in a wide range of formats. Some information may come from older ERP systems, while other datasets are stored in Excel files, CSV exports, XML documents, or even PDF reports. These differences create friction when teams attempt to consolidate and migrate information into Dynamics 365.
Manual reformatting is another common issue. Teams often spend hours adjusting columns, converting formats, or fixing broken structures before files can be imported into the system. This process is time consuming and introduces the risk of human error.
Data silos can also complicate matters. When departments manage their own data independently, inconsistencies appear across the organization. Customer records may differ between sales and finance, product naming conventions may not align, and reporting fields may be structured differently across systems. These issues slow down implementations and create uncertainty around the accuracy of the data that ultimately enters the ERP platform
Why Data Readiness Matters for Reporting and Analytic?
One of the main reasons companies adopt Dynamics 365 is to gain better visibility into their operations. Tools such as Power BI and Jet Reports allow organizations to build dashboards, track performance metrics, and analyze trends across the business.
However, these capabilities depend entirely on the quality and structure of the underlying data. When datasets are inconsistent or poorly formatted, reporting becomes more complicated.
Analysts may spend large amounts of time cleaning or transforming data before it can be used in dashboards. In some cases, key metrics may become unreliable because different departments interpret data fields in different ways. This creates a situation where teams no longer fully trust the reports they rely on to make decisions. By focusing on data readiness early in the implementation process, organizations create a solid foundation for analytics.
Structured and standardized datasets allow reporting tools to function as intended, making it easier to generate insights and monitor business performance
A Practical Approach to Improving Data Readines
Improving data readiness does not require a massive overhaul of existing systems. In many cases, it begins with a structured approach to understanding and preparing the data that will enter Dynamics 365.
The first step is auditing existing data sources. This means identifying where key datasets currently live, what formats they use, and how they relate to each other. During this stage, teams can also detect duplicates, missing values, and inconsistencies that need to be addressed.
Next comes standardizing data formats. Organizations should define clear guidelines for how information such as dates, currencies, naming conventions, and identifiers are structured.
Consistent formatting makes it much easier to import and manage data within Dynamics.
Automation can also play an important role in improving efficiency. Instead of manually adjusting files every time they need to be imported or shared, teams can use tools that quickly convert data into compatible formats.
Solutions such as convert.fast help transform files between formats in seconds, which reduces the manual effort often associated with preparing data for ERP systems.
Before performing full migrations, it is important to validate the data in a test environment. Importing datasets into a sandbox version of Dynamics allows teams to confirm that structures and relationships work as expected.
This step can prevent many of the issues that typically appear during large scale migrations.
Finally, data preparation should be aligned with reporting requirements. If dashboards and analytics are part of the implementation strategy, the data structures should support those use cases from the beginning.
The Role of File Conversion in Data Preparation
File conversion websites like Convert Fast may seem like a small operational detail, but it often plays a surprisingly large role in data readiness.
In many Dynamics projects, data arrives from multiple sources and in different formats. Teams may receive CSV exports from legacy systems, Excel files from finance departments, XML data from integrations, or PDF reports that need to be transformed into structured datasets.
Converting these files manually is not only time consuming but also prone to errors. Even small formatting differences can cause import failures or produce incorrect data relationships within the system.
Using reliable file conversion tools can significantly reduce this friction. When files can be converted quickly and accurately, teams spend less time preparing data and more time focusing on analysis, reporting, and system optimization.
This seemingly simple improvement can help streamline migration processes and keep implementation timelines on track.
The Benefits of High Data Readiness
Organizations that invest time in preparing their data properly often see clear advantages throughout their Dynamics 365 projects.
Implementations tend to move faster because fewer issues appear during migration. Data imports run more smoothly, and teams spend less time troubleshooting formatting errors.
Users also adopt the system more quickly when they trust the data they see. Accurate customer records, product information, and financial data make it easier for employees to rely on the platform in their daily work.
Reporting and analytics become far more powerful as well. Clean and structured datasets allow dashboards to deliver insights that are both timely and reliable. This improves decision making across finance, operations, and management teams.
Over time, these improvements reduce maintenance efforts and help organizations get more value from their ERP investment. Data First, System Second Technology plays an important role in digital transformation, but it cannot compensate for unprepared data. Even the most advanced ERP platform depends on accurate and well structured information to perform effectively.
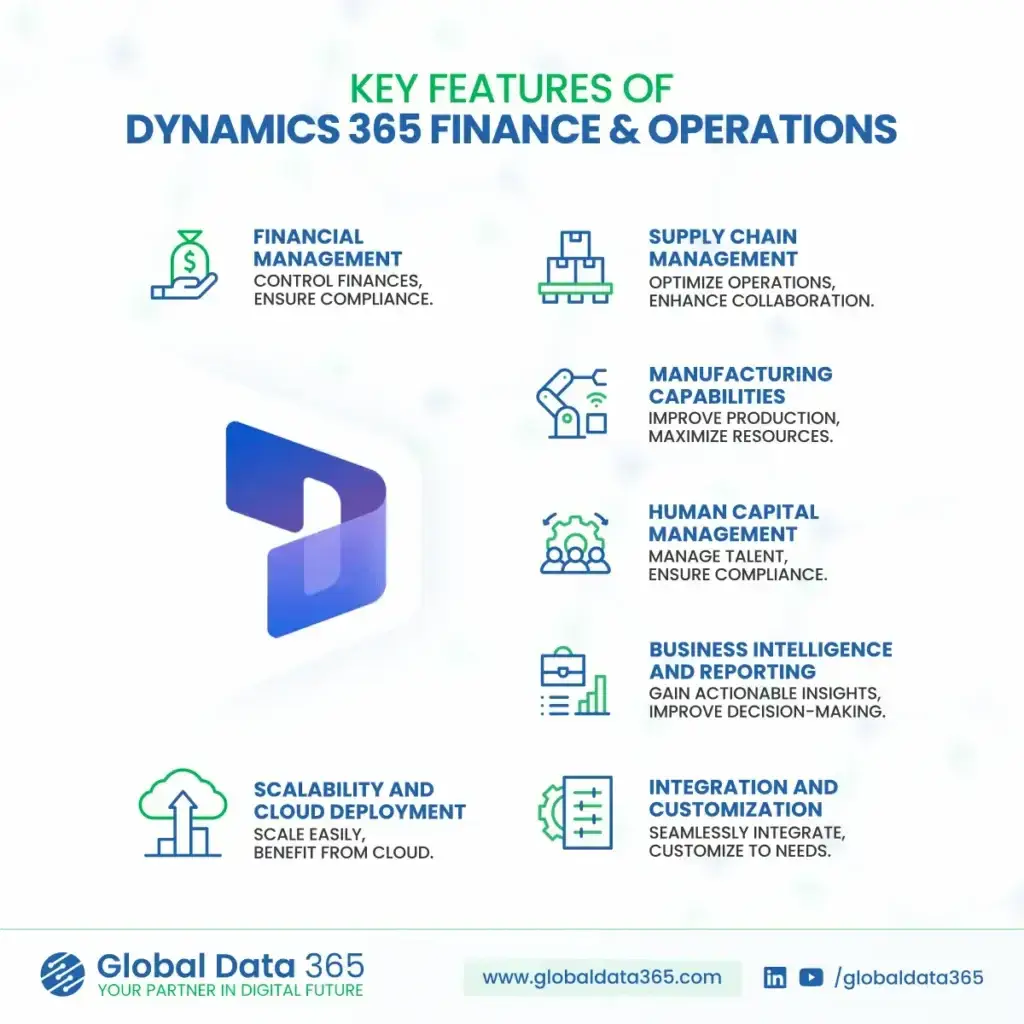
Dynamics 365 offers powerful capabilities for operations, reporting, and analytics. When organizations prioritize data readiness, they create the conditions needed for those capabilities to deliver real business value.
Companies that approach implementation with a data first mindset often experience smoother projects, stronger reporting, and a faster return on their technology investment.
From Data Preparation to ERP Success. Connect with us.
Search Blog
Related Resources
Connect Power BI MCP Server to Claude Desktop


Why Power BI is a Better Choice than Excel for Analytics
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Improving Data Readiness in Dynamics 365 Projects Read More »